Kops: Kops is also known as Kubernetes Operations,
it is an open-source project which helps you to create, upgrade, destroy, and
maintain a highly available, production-grade Kubernetes cluster.
Kops is an automation provisioning system:
a.
Fully Automated installation.
b.
Use DNS to identify clusters.
c.
Self-healing: Everything runs in Auto Scaling
Groups.
d.
Multiple OS Supports (Amazon Linux, Debian,
Flatcar, RHEL, Rocky, and Ubuntu).
e.
Highly Available support.
Pre-Requisites:
a. “AWS CLI” must be installed and must
have an AWS Account and generate AWS Keys and configure them.
Note: if you are using other than Amazon Linux, we must
install AWS CLI. For Amazon Linux images AWS CLI is installed by default.
b. “kubectl” must be installed.
c. “kops” must be installed.
The bootstrap server can be your EC2 instance created in AWS.
A bootstrap server is only needed to set up the K8s cluster by running the kops
commands to initialize the cluster.
Create a bootstrap server:
a.
How
to create an EC2 Instance Link: How
to create an EC2 Instance
b.
How
to connect to an EC2 instance using Putty Client: How
to Connect to an EC2 instance using Putty client
Once you create
the Bootstrap Server and connect it using the Putty client, install the
following packages.
I. Install AWS CLI:
Ø
pip install awscli (or) Install AWS CLI2
Ø
AWS Configure
II. Install kubectl on Linux:
if CURL package not available in
your OS, use the below commands to install CURL.
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt install curl -y
RHEL/Amazon Linux:
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install curl -y
Ø
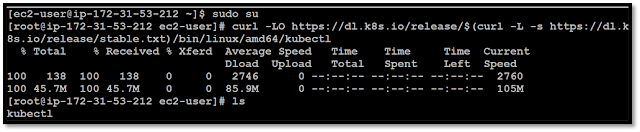
Download the latest release with the command:
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl
-L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
Ø
Validate the binary (optional)
Download the kubectl checksum file:
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl.sha256
Ø Validate the kubectl binary against the checksum file:
echo "$(cat kubectl.sha256) kubectl" | sha256sum –check
If valid, the output is:kubectl: OK
Ø Give executable permission to the downloaded kubectl binary and move it to /usr/local/bin/
chmod +x kubectl
mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
Ø Test to ensure the version you installed is up-to-date:
kubectl version --short or kubectl version --output=yaml
III. How to install Kops.
Ø Download the kOps from the releases
package.
curl -Lo
kops https://github.com/kubernetes/kops/releases/download/$(curl -s
https://api.github.com/repos/kubernetes/kops/releases/latest | grep tag_name |
cut -d ‘”’ -f 4)/kops-linux-amd64
Ø Give executable permission to the downloaded kOps file and move it to /usr/local/bin/
chmod +x kops
Ø Run the kOps command to verify the installation.
kops
$kops version
IV.
Create
IAM Role
Create IAM Role and
attach the role to the bootstrap server. The kops user will require the following
IAM permissions to function properly:
§ AmazonEC2FullAccess
§ AmazonRoute53FullAccess
§ AmazonS3FullAccess
§ IAMFullAccess
§ AmazonVPCFullAccess
§ AmazonEventBridgeFullAccess
§ AmazonSQSFullAccess
IV.
Configure
Route53 (Optional in my case)
A custom domain is required to setup the Kubernetes cluster
using Kops so that Kops can create required resource records in that domain in
Route 53. example – “democluster.devops-learner.com".
Gossip is alternate option if you want to deploy a cluster
without a custom domain in Route 53. To use gossip-based DNS, configure the
cluster domain name to end with.k8s.local. example –
"democluster.k8s.local"
V.
Create
Cluster State Storage (S3 Bucket)
To store
the state of your cluster, and the representation of your cluster, we need to
create a dedicated S3 bucket for kops to use. This bucket will become the
source of truth for our cluster configuration.
create S3
bucket. example bucket – "democluster-k8s-state-store"
IV.
Setup
SSH Keys
Create SSH
Keys by running “ssh-keygen -t rsa”, which creates keys in the default location
$HOME/.ssh
IV.
Create
cluster configuration.
Congratulations!! You have set up all
prerequisites on the bootstrap server.
We’re ready to start creating our k8s
cluster! setup below environment variables to start creating cluster
configuration.
Custom Domain
export NAME= democluster.devops-learner.com
export
KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://democluster-k8s-state-store
I am going with the Gossip Domain.
Gossip Domain
export
NAME=democluster.k8s.local
export
KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://democluster-k8s-state-store
Run below command to create cluster
configuration.
$ kops create cluster --zones=us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c
${NAME}
IV.
Modify
cluster configuration (Optional)
Kops created default cluster
configuration and now you can edit the configuration if needed to customize it
by running below command
V.
Build
a cluster
Run below command to build the
cluster with the configuration that was created in the previous step. Cluster
build takes a while and hence wait for longer until the cluster is ready for
you.
$ kops update cluster ${NAME} --yes --admin
(or)
$kops update cluster --name democluster.k8s.local --yes --admin
Note that, the configuration for your
cluster was automatically generated and written to $HOME/.kube/config for
you! If config was not created then can
export the config using below command
$ kops export kubecfg --admin
IV.
Validate
cluster
The below commands help you to check
your cluster status, If the cluster is not ready wait for a few more minutes
and check again!!
$kops validate cluster
$kubectl
get nodes
IV.
Delete
cluster
IMPORTANT! to note that cluster
resources created by Kops are not in Free Tier, hence you may need to destroy
resources once you are done with the setup.
You can preview all the AWS resources
that will be destroyed when the cluster is deleted by issuing the following
command.
$kops delete cluster --name ${NAME}
Below command to
delete resources
Kops Created cluster with required setup in
the AWS Environment
After Cluster deletion, all Nodes and its
allocated resources got deleted / terminated.
Note: Make sure all the resources
got deleted successfully and S3 bucket should be deleted manually
Pods Events:
Scheduled: Default Schedular will take care of
the Pod should be scheduled to which
Workernode.
Pulling: The docker image pulling from respective
docker hub/repository.
Pulled: The docker image pulled successfully.
Created: Container created for the
application.
Started: The container started for the
application
Pod Running status: